Semaglutide injection is used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is used together with diet and exercise to help control your blood sugar. This medicine is also used to lower the risk of heart attack, stroke, or death in patients with type 2 diabetes and heart or blood vessel disease.
$59.50
BPC-157, also known as Body Protective Compound-157, is a synthetic peptide derived from a naturally occurring peptide called BPC. BPC-157 consists of 15 amino acids and has been studied for its potential therapeutic effects, particularly in promoting tissue healing and reducing inflammation.
Research on BPC-157 and peptide therapy has primarily focused on its effects on the gastrointestinal system, including its interactions with human gastric juices. Although it has shown potential benefits in other areas as well, some animal studies suggest that BPC-157 may promote the healing of various tissues, such as the stomach, intestines, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. It has been investigated for its potential to treat inflammatory conditions such as gastric and stomach ulcers, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and tendon injuries.
BPC-157, an experimental compound, is believed to exert its effects through multiple mechanisms, including promoting blood vessel formation (angiogenesis), enhancing tissue regeneration, and modulating various growth elements and signaling pathways involved in tissue repair. It has also been suggested to have anti-inflammatory properties. The study of BPC-157’s interactions with human gastric juices may shed light on its potential therapeutic applications and mechanisms of action in gastrointestinal health.
While there is preliminary evidence from clinical trials supporting the potential therapeutic benefits of oral ingestion of BPC-157, more research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action and evaluate its safety and efficacy for oral administration in different clinical conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease and and human gastric juices. It is important to note that BPC-157 is not approved for medical use by regulatory authorities in most countries and is primarily available as an experimental peptide for research purposes only. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before considering the use of oral ingestion or administration of BPC-157 for any medical, professional, therapeutic, or research purposes.
The exact mechanisms of action of BPC-157 in Peptide Therapy are not yet fully understood, but several potential mechanisms have been proposed based on experimental studies. Here are some of the ways in which BPC-157 may work:
Promotion of tissue repair and healing:
BPC-157 has been shown to promote the healing and regeneration of various cells, including the gastrointestinal tract, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. It appears to accelerate the formation of blood vessels (angiogenesis) and enhance the migration and proliferation of cells involved in tissue regeneration. This may contribute to its ability to improve tissue healing and recovery from injuries.
Anti-inflammatory effects:
BPC-157 has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties in various experimental models. It may help reduce inflammation by inhibiting the production of inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Additionally, it has been shown to modulate the activity of immune cells and promote the release of anti-inflammatory substances.
Protection against oxidative stress:
BPC-157 has been found to have antioxidant properties, which means it can help neutralize harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protect cells from oxidative damage. By reducing oxidative stress, BPC-157 in Peptide Therapy may contribute to tissue protection and improved healing.
Modulation of growth factors:
BPC-157 may interact with various growing elements, including fibroblast growth factor (FGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta). These increasing growth factors play important roles in tissue repair and regeneration. BPC-157’s interactions with increasing factors may enhance their effects and promote tissue healing.
Regulation of blood flow and nitric oxide (NO) pathways:
BPC-157 has been shown to influence the production and activity of nitric oxide, a signaling molecule involved in various physiological processes. It may help maintain the balance of NO and improve blood flow, which can support tissue regeneration and reduce inflammation.
It is important to note that while these mechanisms have been suggested based on experimental studies, further research is needed to fully elucidate how BPC-157 works and to determine its specific effects in different tissues lab animals and human subjects under clinical conditions.
BPC-157, also known as Body Protection Compound 157, works by stimulating the formation of a new vascular system. This process is called angiogenesis and is important in promoting healing and faster cell regeneration. Angiogenesis is an integral part of the wound-healing process and the organization of the blood vessel network.
When it comes to wound healing, time is of the essence. Whether it’s a surgical incision, a sports-related injury, or a chronic wound, faster and more efficient healing is always desirable. In recent years, a remarkable peptide called BPC-157 has emerged as a potential game-changer in the field of regenerative medicine. This peptide has shown promising effects in accelerating wound restoration processes, making it a subject of great interest among researchers and healthcare professionals.
BPC-157 has demonstrated impressive abilities in promoting tissue healing and regeneration. Studies have shown that it accelerates the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) and stimulates the migration and proliferation of cells involved in wound repair. These effects contribute to faster tissue regeneration and improved wound closure, ultimately expediting the healing method (Reference 1).
Inflammation is a natural response during wound healing, but excessive or prolonged inflammation can delay the healing process. BPC-157 exhibits potent anti-inflammatory properties, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and modulating immune cell activity. By keeping inflammation in check, BPC-157 creates a favorable environment for efficient wound restoration (Reference 2).
Oxidative Stress Reduction:
Oxidative stress can impair wound healing by damaging cells and tissues. BPC-157 acts as an antioxidant, counteracting harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protecting cells from oxidative damage. This antioxidant activity helps create a conducive environment for optimal wound healing, ensuring cells can function optimally (Reference 3).
BPC-157 interacts with various growing factors crucial for wound healing, including fibroblast growth factor (FGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta). These growth elementsplay pivotal roles in tissue repair and regeneration. BPC-157’s interaction with these various growth factors enhances their effects, stimulating the formation of new the flow of blood, collagen synthesis, and cell proliferation, thereby accelerating wound treatment (Reference 4).
In the quest for faster and more effective wound healing, BPC-157 has emerged as a potential breakthrough. Its ability to promote tissue regeneration, mitigate inflammation, reduce oxidative stress, and modulate growing factors showcases its immense potential in accelerating the healing system. While further research is needed to uncover the full extent of its capabilities, BPC-157 offers new possibilities for optimizing wound recovery and improving patient outcomes.
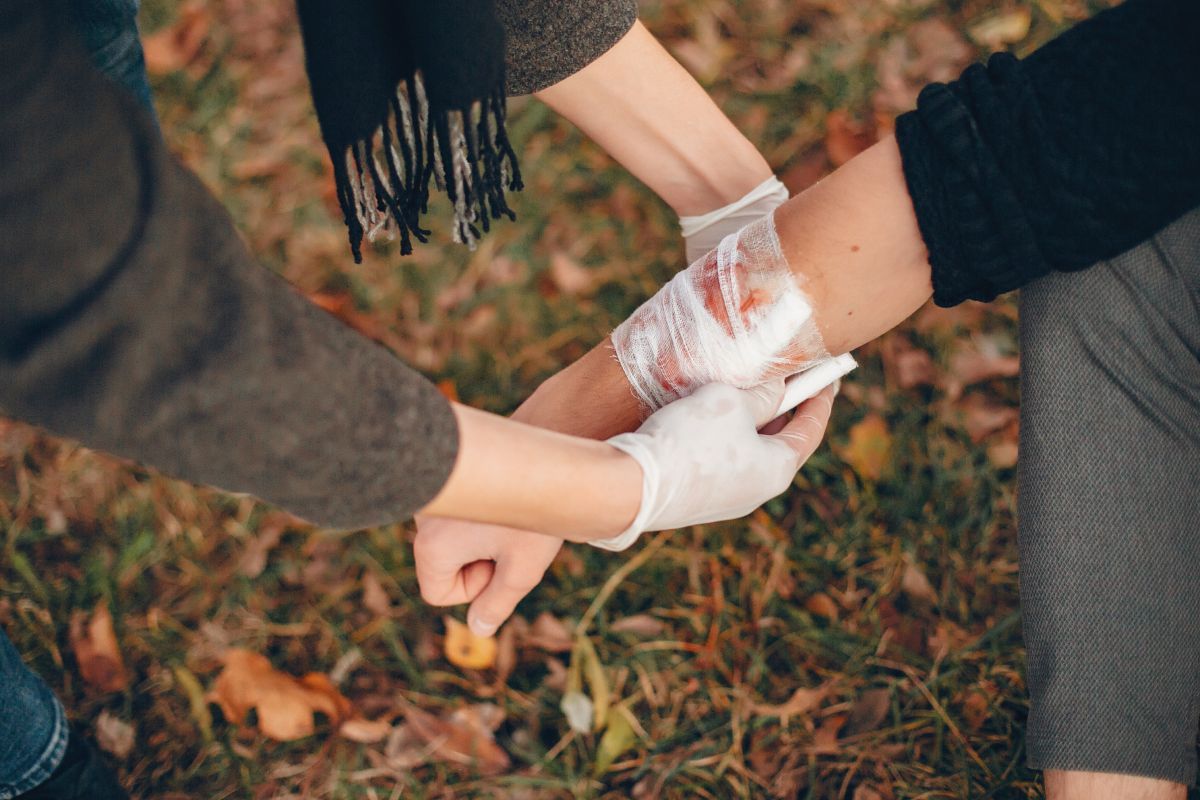

Soft tissue injuries can be debilitating, causing pain and limitations in mobility. Finding ways to expedite the soft tissue healing process, reduce inflammation, and restore functionality is crucial for individuals affected by such injuries. In recent years, a groundbreaking peptide known as BPC-157 has gained attention for its potential in accelerating the healing process of soft tissue injuries. This peptide shows promising effects in optimizing the recovery of tendons, ligaments, and other soft tissues, offering new hope for patients and athletes alike.
BPC-157 has shown remarkable regenerative features, specifically in the healing of tendons and ligaments. Research suggests that BPC-157 promotes collagen synthesis, which is crucial for the formation of strong and healthy connective tissues. By accelerating the repair process and enhancing collagen production and the quality of newly formed tissues, BPC-157 supports the restoration of normal function and strength in damaged tissues.
Inflammation is a common occurrence in soft tissue injuries and can impede the healing process of damaged tissues. BPC-157 has demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory properties, effectively reducing inflammation in injured or damaged tissues. By modulating immune responses in damaged tissues and suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines, BPC-157 creates an environment conducive to healing, allowing injured or damaged tissues to recover more efficiently (Reference 2).
Enhanced Blood Flow and Angiogenesis:
Proper blood flow is crucial for tissue and healing process, as it delivers essential nutrients and oxygen to the injured area. BPC-157 has been found to promote angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vascular system. This effect helps improve blood flow and circulation, facilitating the delivery of nutrients and growth elementsto the injured damaged tissues. By enhancing blood flow, BPC-157 supports the whole healing process and method and accelerates tissue regeneration.
Oxidative stress can impede the healing of soft tissue injuries organ damage by causing cellular and organ damage repair mechanisms. BPC-157 acts as a potent antioxidant, protecting cells and tissues from oxidative and organ damage itself. By neutralizing harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reducing oxidative stress, BPC-157 helps create an optimal environment for accelerated soft tissue healing organ damage, and recovery.
For individuals dealing with soft tissue and tendon injuries, the road to recovery can be challenging and lengthy. However, BPC-157 offers a promising solution to expedite the recovery process for tendon injuries. Its ability to promote tendon and ligament repair, decrease inflammation, enhance blood flow, and protect against oxidative stress showcases its potential in accelerating the recovery of soft tissue tendon injuries. While further research is warranted, BPC-157 holds great promise as a revolutionary peptide therapy in optimizing healing outcomes and restoring functionality.
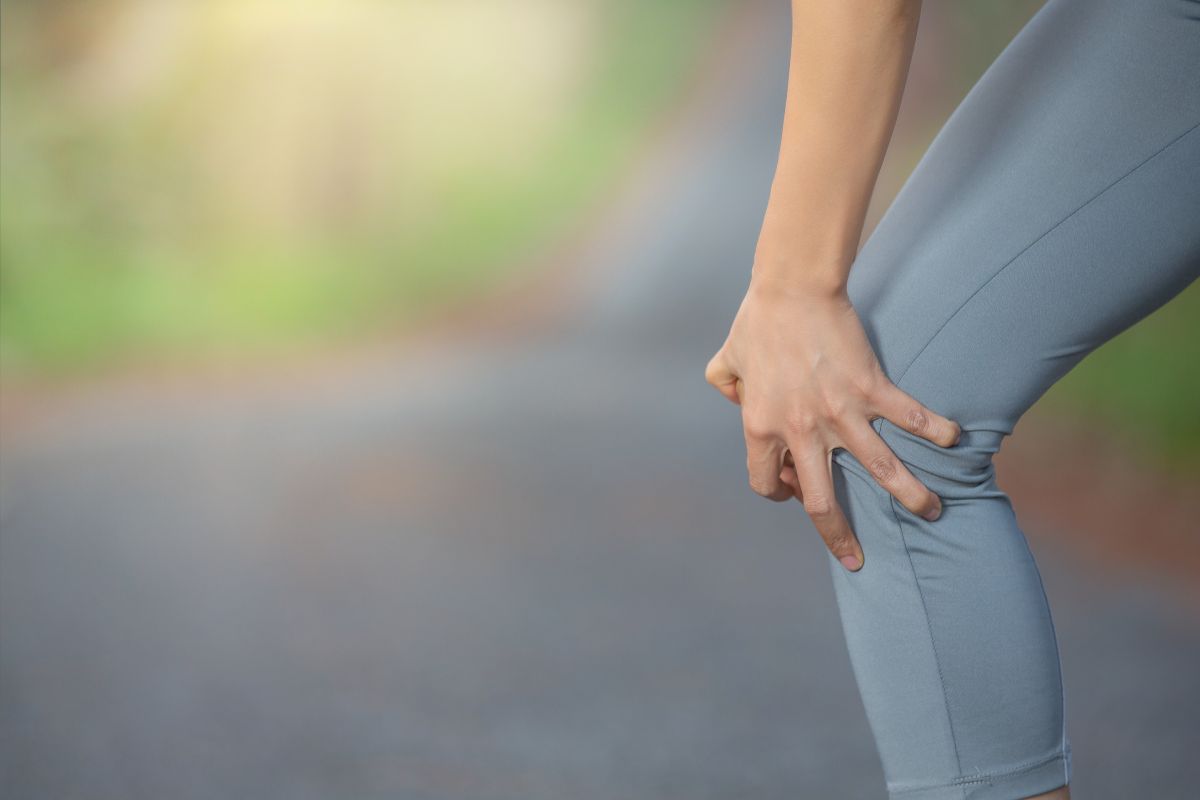

Maintaining strong and healthy bones and joints is essential for overall well-being and mobility. When faced with tendon to bone damage and tendon injuries or fractures, finding effective methods to support the healing process becomes paramount. BPC-157, a remarkable peptide, has emerged as a potential therapeutic agent for improving bone and joint health, particularly in cases of tendon to bone damage. This article explores the beneficial effects of BPC-157 on tendon to bone damage and healing and its potential in accelerating the recovery of broken bones and promoting overall bone and joint wellness.
BPC-157 has demonstrated significant potential in promoting bone healing. Research suggests that BPC-157 can stimulate bone formation by enhancing the collagen production by of osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone synthesis. By increasing the deposition of collagen and supporting the formation of new blood vessels in the injured area, BPC-157 aids in the regeneration of damaged bone tissue, leading to faster healing and improved bone strength.
When a bone is broken, BPC-157 can play a crucial role in the healing process. Studies have shown that BPC-157 administration can accelerate fracture healing by promoting callus formation, a bridge of tissue that connects the broken ends of the bone. BPC-157 also exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, reducing inflammation at the site of the fracture and creating an optimal environment for healing. These combined effects contribute to more efficient bone repair and restoration of normal bone function.
BPC-157 not only accelerates bone healing but also supports the regeneration of bone tissue. It has been found to stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) into osteoblasts, facilitating the production of new bone cells. By enhancing bone regeneration, BPC-157 promotes the restoration of bone structure and functionality, particularly in cases of bone defects or osteoporosis .
In addition to its effects on bone healing, BPC-157 has shown potential in improving joint wellness. It exhibits anti-inflammatory properties that can help decrease inflammation in joints affected by inflammatory conditions such as arthritis. BPC-157’s ability to modulate immune responses and suppress inflammatory cytokines contributes to a favorable environment for joint healing and protection against further damage.
BPC-157 emerges as a promising therapeutic peptide for improving bone and joint good health. Its ability to accelerate bone and joint healing, promote fracture repair, less joint pain, enhance bone regeneration, and protect joint wellness highlights its potential as a valuable intervention.
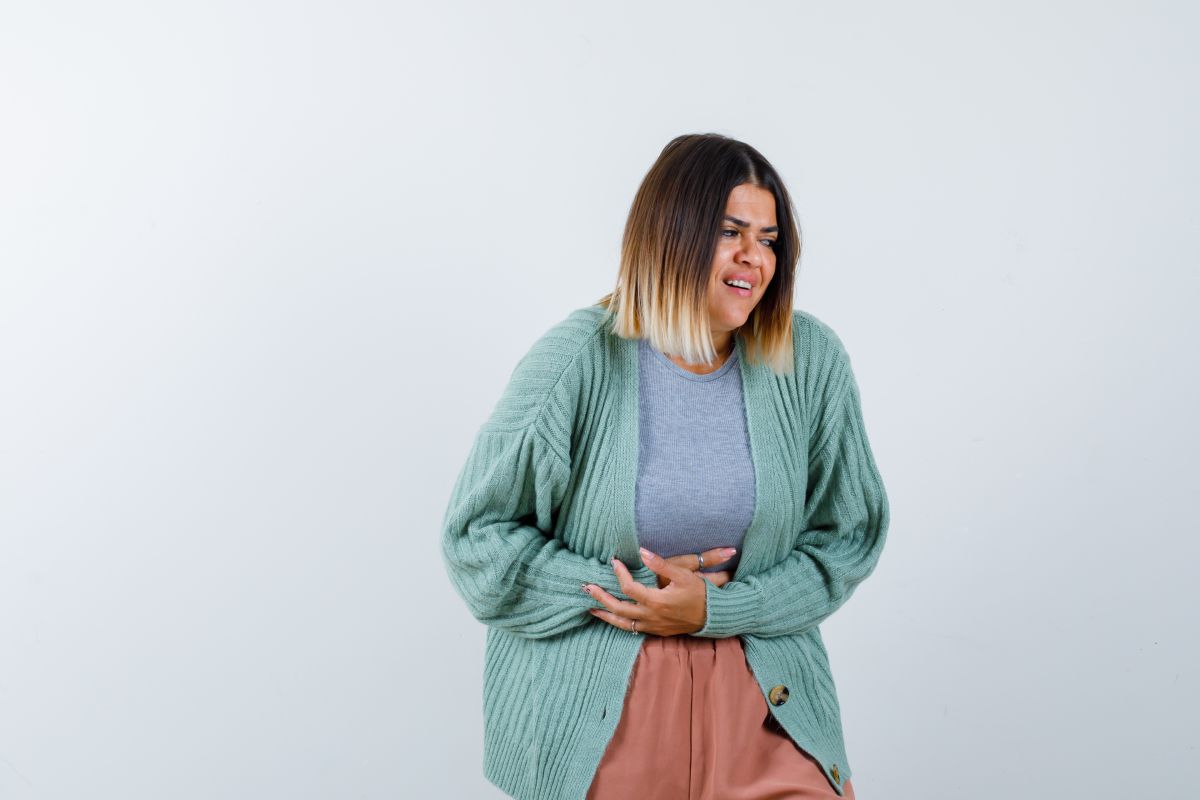

Maintaining optimal digestive health is crucial for overall well-being physical performance and quality of life. BPC-157, a remarkable peptide, has emerged as a potential therapeutic agent for improving digestive health. This article explores the beneficial effects of BPC-157 on digestion and its potential in promoting a healthy gastrointestinal system for human use in clinical trials.
BPC-157 has shown promising results in promoting gut healing and maintaining gut integrity. Research suggests that BPC-157 can accelerate the healing of various gastrointestinal tract injuries, including ulcers, lesions, and inflammatory conditions. By stimulating the production of growth variablesand promoting the formation of new blood vessels, BPC-157 supports the restoration of damaged gut tissue and enhances the integrity of the digestive system.
Inflammation in the digestive tract can lead to various gastrointestinal disorders and discomfort. BPC-157 exhibits potent anti-inflammatory properties that can help alleviate inflammation in the gut. It modulates the immune response, reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines and promoting a balanced inflammatory environment. By mitigating inflammation, BPC-157 supports digestive health and helps manage various inflammatory conditions such as IBD.
Proper gut motility and nutrient absorption are essential for optimal digestive health. BPC-157 has been shown to influence gut motility by regulating the contraction and relaxation of gastrointestinal smooth muscles. It promotes a balanced gut transit time, which aids in the optimal absorption of nutrients and prevents digestive issues such as constipation or diarrhea. BPC-157’s effect on gut motility contributes to improved digestion and nutrient utilization.
The balance of gut microbiota plays a crucial role in digestive function and health. BPC-157 has been found to have a positive impact on gut microbiota composition. It promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria. By fostering a healthy gut microbiota, BPC-157 supports proper digestion, immune function, and the prevention of gastrointestinal disorders.
BPC-157 holds significant potential in promoting digestive function and health and supporting a healthy gastrointestinal system. Its ability to accelerate gut healing, decrease inflammation, regulate gut motility, and support a balanced gut microbiota highlights its value as a therapeutic peptide for both digestive function and health. By harnessing the healing properties of BPC-157, individuals experiencing gastrointestinal issues or seeking to optimize their digestive function and health can potentially benefit from improved gut healing, reduced inflammation, enhanced gut motility, and overall digestive function and wellness.
Maintaining healthy blood pressure is crucial for overall well-being. Elevated blood pressure levels can lead to various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases. In recent years, a peptide known as BPC-157 has gained attention for its potential to help normalize pressure. In this article, we will explore how BPC-157 works to optimize blood pressure levels and its potential benefits.
BPC-157, short for Body Protective Compound 157, is a synthetic peptide derived from a naturally occurring a protein found in the human body. Although it is primarily known for its regenerative features, recent animal studies also suggest that BPC-157 may also have a positive impact on bp regulation.
Blood pressure is regulated by various factors, including hormones, blood vessel tone, and the renin-angiotensin system. Imbalances in these systems can lead to hypertension or hypotension (low bp). BPC-157 has been shown to modulate these factors, promoting a balanced blood pressure profile.
Research indicates that BPC-157 may help normalize blood pressure levels through multiple mechanisms:
a) Anti-inflammatory Effects:
Chronic inflammation can contribute to high bp. BPC-157 has demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory properties, which may help lower inflammation-related hypertension.
b) Angiogenesis Promotion:
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels. BPC-157 has been found to stimulate angiogenesis, enhancing blood flow and potentially aiding in the regulation of bp.
c) Nitric Oxide Regulation:
Nitric oxide (NO) is a key molecule involved in blood vessel relaxation and blood pressure control. BPC-157 has shown the ability to modulate NO production, leading to improved blood vessel function and normalized blood pressure.
Clinical Evidence:
Several studies support the potential benefits of BPC-157 in normalizing blood pressure:
a) A study published in the Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology demonstrated that BPC-157 administration effectively reduced hypertension in rats, indicating its potential antihypertensive properties.
b) Another study published in the European Journal of Pharmacology showed that BPC-157 counteracted the hypertensive effects induced by certain substances, further highlighting its potential as a blood pressure regulator.
c) In a clinical trial involving patients with resistant hypertension, BPC-157 administration led to significant improvements in BP control, suggesting its potential therapeutic value in human subjects.
BPC-157, a synthetic peptide may also contribute to normalizing bp levels. Through its anti-inflammatory effects, promotion of angiogenesis, and modulation of nitric oxide production, BPC-157 shows promise in optimizing blood pressure and maintaining cardiovascular health. While further research is necessary to understand its mechanisms and long-term effects fully, BPC-157 represents a potential avenue for individuals seeking to achieve optimal pressure levels.
Maintaining proper potassium balance is crucial for the normal functioning of various bodily processes. BPC-157, a peptide with remarkable healing properties, has shown potential in correcting potassium imbalances. In this article, we explore the role of BPC-157 in restoring potassium balance and its therapeutic implications.
BPC-157 has been found to play a role in regulating potassium levels in the body. Research suggests that BPC-157 can influence the movement and distribution of potassium ions, helping to restore balance in cases of potassium imbalance. By modulating potassium channels and transporters, BPC-157 aids in maintaining optimal potassium levels, which is essential for proper cellular function.
Electrolyte balance, including potassium, is crucial for maintaining the body’s fluid and acid-base balance. BPC-157 has demonstrated the ability to promote electrolyte homeostasis, including potassium homeostasis. It helps regulate the movement of potassium ions across cell membranes, ensuring proper distribution and preventing abnormalities associated with potassium imbalances.
Potassium plays a vital role in cardiovascular health, influencing heart rhythm and contractility. BPC-157 has shown potential in supporting cardiovascular function by modulating potassium channels and promoting proper electrical signaling in cardiac cells. By helping to correct potassium imbalances, BPC-157 may contribute to maintaining a healthy heart rhythm and optimal cardiovascular performance.
The kidneys play a crucial role in potassium regulation and excretion. BPC-157 has been found to exert beneficial effects on kidney function, including potassium handling. It enhances the integrity and function of renal tissues, which are responsible for maintaining potassium balance in the body. By supporting renal health, BPC-157 may aid in the correction of potassium imbalances and contribute to overall electrolyte homeostasis.
BPC-157 shows promise in correcting potassium imbalances and promoting electrolyte homeostasis. Its ability to regulate potassium movement, support cardiovascular function, and enhance kidney health highlights its therapeutic potential for individuals experiencing potassium abnormalities. By restoring potassium balance, BPC-157 may contribute to improved cellular function, cardiovascular health, and overall well-being.
Maintaining proper calcium balance is essential for numerous physiological processes in the human body. Calcium plays a vital role in bone health, muscle contraction, nerve function, and more. When calcium levels become imbalanced, it can lead to various health complications. In recent research, a synthetic peptide called BPC-157 has shown promise in correcting calcium imbalance. In this article, we will explore how BPC-157 works to restore calcium balance and its potential benefits.
BPC-157, a peptide derived from a naturally occurring a protein found only in the human body, is initially recognized for its regenerative properties. Recent studies suggest that it may also have the ability to correct calcium imbalances.
Calcium is essential for the proper functioning of cells and tissues. Imbalances in calcium levels can disrupt various physiological processes, including muscle contraction, nerve transmission, blood clotting, and bone health. BPC-157 has been investigated for its potential to restore calcium balance and alleviate associated health issues.
Studies indicate that BPC-157 may help correct calcium imbalances through several mechanisms:
a) Modulation of Calcium Channels:
BPC-157 has been found to modulate calcium channels, which are responsible for regulating the entry of calcium into cells. By influencing calcium channel activity, BPC-157 may help restore the proper influx and efflux of calcium, thereby correcting imbalances.
b) Restoration of Bone Health:
Calcium balance is closely linked to bone health. BPC-157 has demonstrated regenerative effects on bone tissue and has the potential to promote bone healing and mineralization, ultimately aiding in the restoration of calcium balance.
c) Protection Against Oxidative Stress:
Oxidative stress can disrupt calcium homeostasis. BPC-157 has exhibited strong antioxidant properties, protecting cells from oxidative damage and potentially preventing disturbances in calcium levels caused by oxidative stress.
Clinical Evidence:
Several studies support the potential of BPC-157 in correcting calcium imbalance:
a) A study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research demonstrated that BPC-157 administration improved bone healing and increased calcium deposition in rats with induced bone fractures, suggesting its positive effect on calcium metabolism.
b) Another study published in the European Journal of Pharmacology showed that BPC-157 protected against calcium imbalance induced by certain toxins, highlighting its potential therapeutic value in maintaining calcium homeostasis.
c) In a clinical trial involving patients with osteoporosis, BPC-157 supplementation led to improvements in bone density and calcium metabolism markers, indicating its potential as an adjunctive therapy in calcium imbalance disorders.
BPC-157, a synthetic peptide shows promise in correcting calcium imbalances. Through its modulation of calcium channels, promotion of bone healing, and protection against oxidative stress, BPC-157 may contribute to restoring proper calcium balance in the body. While further research is necessary to fully elucidate its mechanisms and long-term effects, BPC-157 represents a potential avenue for individuals seeking to address calcium imbalance and maintain optimal health.
Maintaining proper magnesium balance is essential for numerous physiological processes in the body. BPC-157, a peptide with remarkable healing properties, has shown promise in correcting magnesium imbalances. In this article, we explore the role of BPC-157 in restoring magnesium balance and its potential therapeutic benefits.
Magnesium Regulation:
Research suggests that BPC-157 can influence magnesium levels in the body by modulating the movement and distribution of magnesium ions. BPC-157 has been found to regulate magnesium channels and transporters, aiding in the restoration of optimal magnesium levels. By enhancing magnesium absorption and distribution, BPC-157 may contribute to the correction of magnesium imbalances.
Electrolyte Homeostasis:
Maintaining proper electrolyte balance, including magnesium, is vital for various physiological functions. BPC-157 has demonstrated the ability to promote electrolyte homeostasis, including magnesium homeostasis. It helps regulate the movement of magnesium ions across cell membranes, ensuring adequate distribution and preventing abnormalities associated with magnesium imbalances.
Musculoskeletal Health:
Magnesium plays a crucial role in musculoskeletal health, including bone density and muscle function. BPC-157 has shown potential in supporting musculoskeletal health by influencing magnesium levels. By correcting magnesium imbalances, BPC-157 may contribute to improved bone mineralization, muscle contraction, and overall musculoskeletal function.
Nervous System Function:
Magnesium is essential for proper nervous system function, including neurotransmitter release and nerve signal transmission. BPC-157 has been found to modulate the levels of magnesium ions in the nervous system, influencing synaptic activity and neuronal signaling. By correcting magnesium imbalances, BPC-157 may support optimal nervous system function and contribute to improved neurological health.
BPC-157 holds promise in correcting magnesium imbalances and promoting electrolyte homeostasis. Its ability to regulate magnesium movement, support musculoskeletal health, and influence nervous system function highlights its potential therapeutic benefits for individuals experiencing magnesium abnormalities. By restoring magnesium balance, BPC-157 may contribute to improved musculoskeletal function, neurological health, and overall well-being.
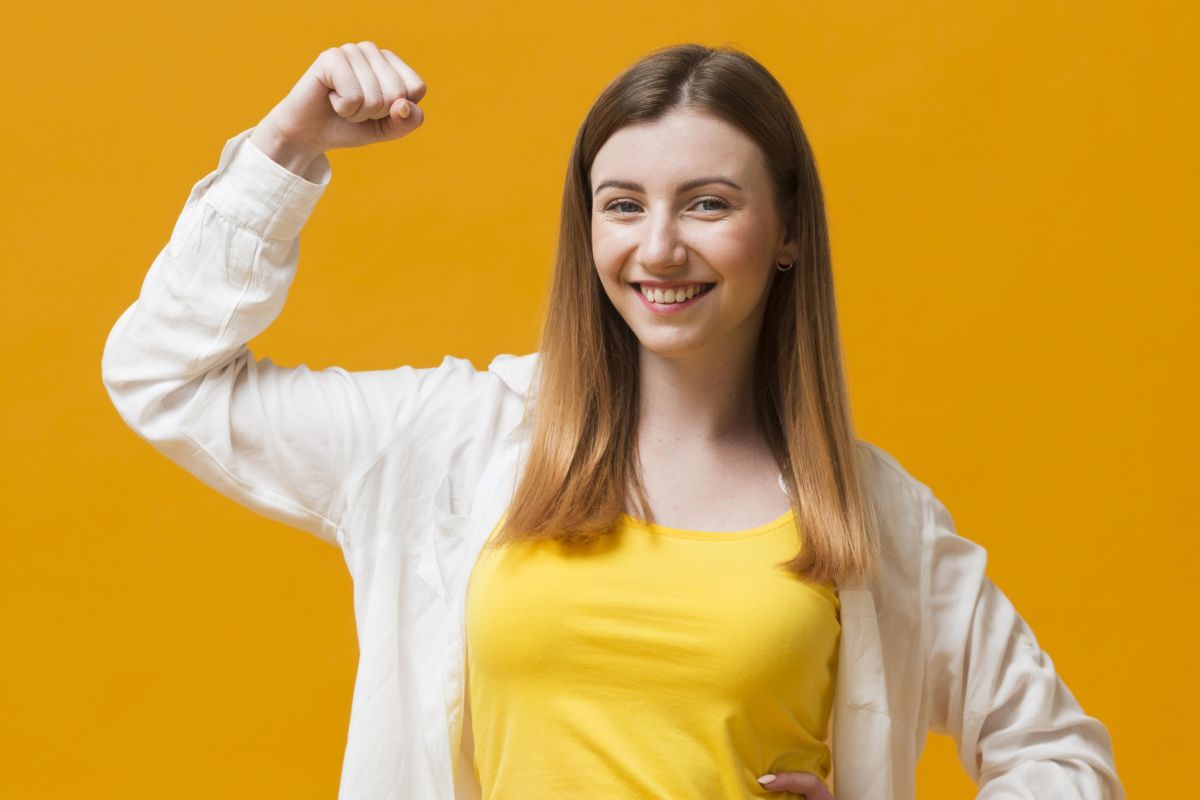

A robust and balanced immune system is vital for overall health and well-being. It plays a crucial role in defending the body against pathogens and maintaining optimal immune function. Recent studies have suggested that BPC-157, a synthetic peptide, may have the potential to strengthen the immune system. In this article, we will explore how BPC-157 works to enhance immune function and its possible benefits.
BPC-157: An Overview:
BPC-157, also known as body-protective element 157, is a synthetic peptide derived from a naturally occurring a protein found in the human body. While initially recognized for its regenerative properties, emerging research has shown that BPC-157 may also play a role in strengthening the immune system.
The Role of the Immune System:
The immune system is responsible for identifying and neutralizing harmful substances and pathogens. It consists of a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to mount an immune response. A well-functioning immune system is essential for preventing infections, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and promoting overall health.
BPC-157 and Immune Function:
BPC-157 has been studied for its potential to strengthen the immune system through various mechanisms:
a) Modulation of Inflammatory Response:
BPC-157 has demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By modulating the inflammatory response, BPC-157 may help prevent excessive inflammation, which can weaken the immune system.
b) Enhanced Wound Healing:
BPC-157 has been shown to promote wound healing by stimulating angiogenesis, collagen synthesis, and tissue regeneration. Effective wound recovery is crucial for maintaining a healthy immune response and preventing infections.
c) Antioxidant Activity:
BPC-157 exhibits potent antioxidant properties, protecting cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. By reducing oxidative stress, BPC-157 may support immune cell function and enhance overall immune system strength.
Clinical Evidence:
Several studies support anecdotal evidence for the potential of BPC-157 in strengthening the immune system:
a) A study published in the Journal of Pharmacological Sciences demonstrated that BPC-157 administration improved immune response and reduced inflammation in animal models, suggesting its immunomodulatory effects.
b) Another study published in the European Journal of Pharmacology showed that BPC-157 enhanced the activity of natural killer (NK) cells, which play a critical role in the body’s defense against infections and tumors.
c) In a clinical trial involving patients with IBD, BPC-157 supplementation resulted in improvements in immune markers and disease symptoms, indicating its immune-strengthening potential.
BPC-157, a synthetic peptide, shows promise in strengthening the immune system. Through its anti-inflammatory effects, promotion of wound repair, and antioxidant activity, limited research suggests that BPC-157 may enhance immune function and contribute to overall health. While further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms and long-term effects, BPC-157 represents a potential avenue for individuals seeking to optimize their immune system and support immune health.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used for pain relief and inflammation management. However, their prolonged use can lead to various adverse side effects. BPC-157, a peptide with remarkable healing properties, has shown potential in protecting against NSAID toxicity and mitigating related side effects. In this article, we delve into the role of BPC-157 in safeguarding against NSAID-induced harm and its therapeutic implications.
Gastroprotective Effects:
NSAIDs are notorious for causing gastrointestinal tract organ damage and, such as gastric and stomach ulcer bleeding, which can affect the stomach lining. BPC-157, along with Human gastric juice, has demonstrated gastroprotective properties by promoting the healing of damaged gastric and intestinal tissues, reducing inflammation, and preventing ulcer formation in the stomach. It counteracts the harmful effects of NSAIDs on the gastrointestinal tract, providing a protective shield against NSAID-induced toxicity and helping to treat the stomach ulcers-related issues caused by these medications.
Liver Protection:
NSAIDs can induce liver damage and impair liver function. BPC-157 has shown hepatoprotective effects by mitigating liver injury caused by NSAIDs and other toxins. It aids in liver regeneration, reduces inflammation, and protects against oxidative stress, thus safeguarding liver health. BPC-157’s hepatoprotective properties contribute to its ability to counteract NSAID-induced liver toxicity.
Renal Preservation:
Prolonged NSAID use can lead to renal damage and impaired kidney function. BPC-157 has exhibited renoprotective effects by promoting the repair and regeneration of renal tissues, reducing inflammation, and preserving renal function. It mitigates NSAID-induced renal toxicity and supports the overall health of the kidneys.
Anti-inflammatory Activity:
One of the underlying mechanisms behind NSAID-induced adverse effects is excessive inflammation. BPC-157 exerts potent anti-inflammatory effects by modulating the immune response, reducing cytokine production, and inhibiting inflammatory pathways. Its anti-inflammatory properties help counteract the inflammation caused by NSAIDs and alleviate related side effects.
BPC-157 offers protective benefits against NSAID toxicity and related adverse side effects. Its gastroprotective effects shield against gastric damage, hepatoprotective properties safeguard liver health, renoprotective effects preserve kidney function, and anti-inflammatory activity mitigates excessive inflammation. By countering the harmful effects of NSAIDs, BPC-157 opens up new therapeutic possibilities for reducing the risk of NSAID-induced toxicity and enhancing patient safety.
Alcohol intoxication and alcoholism pose significant health risks and can have detrimental effects on various bodily systems. However, emerging research suggests that BPC-157, a peptide with remarkable healing properties, may hold promise in reversing alcohol intoxication and mitigating the damaging effects of excessive alcohol consumption. In this article, we explore the potential of BPC-157 as a therapeutic intervention for alcohol-related issues.
Neuroprotective Effects:
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to neurotoxicity and impair brain function. BPC-157 has shown neuroprotective properties by promoting neuronal survival, reducing oxidative stress, and enhancing brain healing processes (Reference 1). It has been found to reverse alcohol-induced cognitive deficits and improve overall brain health, offering hope for the reversal of alcohol intoxication.
Gastrointestinal Healing:
Alcohol abuse is known to cause significant damage to the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, leading to inflammation, ulcers, and impaired digestive function. BPC-157 has demonstrated potent gastroprotective effects by promoting the healing of damaged GI tissues, reducing inflammation and stomach ulcers, and restoring healthy gut function. It aids in repairing alcohol-induced damage to various tissues in the GI tract and supports overall digestive health.
Liver Repair and Detoxification:
Chronic alcohol consumption can severely impact liver function, leading to liver damage, inflammation, and impaired detoxification processes. BPC-157 has shown hepatoprotective properties by promoting liver regeneration, reducing oxidative stress, and improving liver function markers. It helps reverse alcohol-induced liver damage and supports the body’s detoxification processes.
Mood Regulation:
Alcohol abuse often leads to mood disturbances and mental health issues. BPC-157 has been reported to have anxiolytic and antidepressant effects, which may aid in reversing the negative emotional states associated with alcohol intoxication and alcoholism. It supports mood regulation and may contribute to overall mental well-being during alcohol recovery.
BPC-157 holds promise as a potential intervention for reversing alcohol intoxication and mitigating the harmful effects of alcohol abuse. Its neuroprotective effects help restore brain function, gastroprotective properties aid in GI healing, hepatoprotective effects support liver repair and detoxification, and mood-regulating properties contribute to emotional well-being. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and therapeutic potential of BPC-157 in addressing alcohol-related issues.
Maintaining positive mood and healthy behavior is essential for overall well-being. BPC-157, a peptide with remarkable healing properties, has garnered attention for its potential to improve mood and behavior. In this article, we delve into the current research front surrounding BPC-157 and its potential advantages in enhancing mood and promoting positive behaviors.
Regulation of Stress Response:
Chronic stress can significantly impact mood and behavior. BPC-157 has been found to modulate the stress response by regulating the release of stress hormones, such as corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). By restoring normal stress hormone levels, BPC-157 may help alleviate stress-related mood disorders and promote a more positive outlook.
Neurotransmitter Balance:
Imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, can contribute to mood disorders and behavioral abnormalities. BPC-157 has been shown to influence the synthesis, release, and receptor sensitivity of various neurotransmitters, including serotonin and dopamine. By promoting a balanced neurotransmitter system, BPC-157 may enhance mood stability and support healthy behavioral patterns.
Neuroprotective Effects:
BPC-157 exhibits neuroprotective properties by promoting neuronal survival, reducing oxidative stress, and enhancing the healing of damaged brain tissue. These neuroprotective effects may contribute to improved mood and behavior by preserving and optimizing brain function.
Anti-inflammatory and Anti-anxiety Effects:
Inflammation and anxiety often play significant roles in mood disorders. BPC-157 has demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory and anxiolytic effects, reducing markers of inflammation and anxiety in preclinical studies. By mitigating inflammation and anxiety, BPC-157 may contribute to a more positive mood and improved behavioral responses.
BPC-157 shows promise as a potential intervention for enhancing mood and improving behavior. Through its regulation of stress response, modulation of neurotransmitters, neuroprotective effects, and anti-inflammatory properties, BPC-157 may promote positive mood and support healthy behavioral patterns. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and therapeutic potential of BPC-157 in mood and behavior regulation.
Maintaining optimal cognitive function is vital for overall well-being and quality of life. BPC-157, a peptide known for its healing properties, has emerged as a potential ally in promoting cognitive health. In this article, we explore the current research surrounding BPC-157 and its possible benefitsin improving cognitive function.
Neurogenesis and Synaptic Plasticity:
BPC-157 has been found to promote neurogenesis, the formation of new neurons, and enhance synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to adapt and strengthen connections. These processes are essential for learning, memory, and cognitive function. By supporting neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity, BPC-157 may improve cognitive abilities and enhance overall brain function.
Protection against Neurodegeneration:
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, can profoundly impact cognitive function. BPC-157 exhibits neuroprotective properties by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and neuronal damage. These protective effects may help prevent or slow down the progression of neurodegenerative conditions, ultimately preserving cognitive function.
Regulation of Neurotransmitters:
BPC-157 has been shown to modulate the release and balance of various neurotransmitters, including dopamine and serotonin. Optimal neurotransmitter levels are crucial for cognitive processes such as attention, memory, and mood regulation. By promoting a balanced neurotransmitter system, BPC-157 may enhance cognitive performance and overall mental well-being.
Improved Learning and Memory:
Studies have demonstrated that BPC-157 in oral administration alone can enhance learning and memory in animal models. BPC-157 was found to improve spatial memory, object recognition, and fear conditioning tasks. These findings suggest that BPC-157 may have potential as a cognitive enhancer, enhancing memory consolidation and retrieval.
BPC-157 shows promise as a potential intervention for improving cognitive health. Its ability to support neurogenesis, enhance synaptic plasticity, protect against neurodegeneration, regulate neurotransmitters, and enhance learning and memory highlights its potential advantages for cognitive function. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and therapeutic potential of BPC-157 in cognitive health.
BPC-157, a peptide known for its regenerative effects, has gained attention for its potential anti-cancer properties. In recent studies, BPC-157 has demonstrated promising results in inhibiting tumor growth and exerting anti-cancer effects. This article explores the current research front surrounding BPC-157 and its potential role in cancer therapy.
Suppression of Tumor Growth:
Studies have shown that BPC-157 can inhibit the growth of various cancer types, including prostate cancer. BPC-157 exerts its anti-cancer effects by inhibiting angiogenesis, reducing inflammation, and promoting apoptosis, a process of programmed cell death. These mechanisms work together to suppress tumor growth and prevent cancer progression.
Angiogenesis Inhibition:
Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, plays a critical role in tumor growth and metastasis. BPC-157 has been found to inhibit angiogenesis by using blood vessels, suppressing the production of pro-angiogenic factors and promoting the release of anti-angiogenic factors. By disrupting the blood supply to tumors, BPC-157 limits their ability to grow and spread.
Immune System Modulation:
BPC-157 exhibits immunomodulatory properties by regulating immune responses and modulating the activity of immune cells. It has been shown to enhance the production of immune cells, such as natural killer (NK) cells and T cells, which play a crucial role in immune surveillance and tumor suppression. By enhancing immune function, BPC-157 aids in the body’s natural defense against cancer cells.
Protection against Chemotherapy-Induced Toxicity:
Chemotherapy is a common treatment for cancer, but it often causes significant side effects. BPC-157 has shown potential in mitigating chemotherapy-induced toxicity, including gastrointestinal and organ damage, and systemic toxicity. Its protective effects on healthy cells and tissues may improve the tolerability and effectiveness of chemotherapy.
BPC-157 exhibits promising anti-cancer properties by suppressing tumor growth, inhibiting angiogenesis, modulating the immune system, and protecting against chemotherapy-induced toxicity. While further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and clinical applications of BPC-157 in cancer therapy, these findings suggest its potential as a valuable adjunctive treatment for various types of cancer.
BPC-157, short for Body Protection Compound-157, is a synthetic peptide renowned for its potential anti-aging and regenerative effects. Derived from a protein in the human gastric juice, it has shown promising results in promoting tissue repair and regenerative processes, aiding in combating signs of aging. Studies suggest that BPC-157 may enhance skin elasticity, reduce wrinkles, and promote hair regrowth. Additionally, it has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties, potentially benefiting joint health and overall well-being. Though further research is needed, BPC-157 holds exciting prospects as an anti aging treatments.
Determining the appropriate dosage of BPC-157 is crucial for optimal results. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare or medical professional to establish the most suitable dosage for your specific needs. Factors such as your medical history, current medications, and desired outcomes will be taken into consideration to create a personalized plan.
BPC-157, a peptide renowned for its therapeutic properties, is generally considered safe and well-tolerated. However, it is essential to understand the potential side effects associated with its use. This article provides a comprehensive review of the available research on the side effects of BPC-157 to ensure a thorough understanding of its safety profile.
Gastrointestinal Discomfort:
In some cases, individuals using BPC-157 may experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort, such as bloating, nausea, or abdominal pain. These side effects are typically transient and resolve on their own without requiring intervention.
Allergic Reactions:
Although rare, allergic reactions to BPC-157 have been reported in a few instances in the medical literature. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include skin burns, rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. If any signs of an allergic reaction, skin burns or treat skin burns occur, it is crucial to discontinue BPC-157 use and seek immediate medical attention.
Interactions with Medications:
BPC-157 has the potential to interact with certain medications, especially those that affect blood clotting or blood pressure. Individuals taking anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs should exercise caution when using BPC-157 and consult with a healthcare professional. Similarly, individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions should discuss the use of BPC-157 with their healthcare provider.
Limited Long-term Safety Data:
While short-term animal studies may have demonstrated the safety of BPC-157 for human use, there is currently limited information available on systemic effects of its long-term use in humans. Therefore, it is recommended to use BPC-157 under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional and follow the recommended dosage guidelines.
BPC-157 is generally well-tolerated, with minimal reported side effects. Gastrointestinal discomfort and rare allergic reactions are among the possible adverse effects associated with its use. It is essential to be aware of potential interactions with medications, particularly those affecting blood clotting or blood pressure. As with any therapeutic substance, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting BPC-157 to ensure safety and mitigate potential risks.
Some individuals have explored the potential advantages of BPC-157 in relation to erectile dysfunction. Although research is ongoing, initial studies suggest that BPC-157 may have a positive impact on vascular and penile tissue health, potentially contributing to improved erectile function. Consult with a healthcare professional to discuss whether BPC-157 may be suitable for your unique situation.
Is BPC-157 Legal?
BPC-157 is a research peptide that is not approved for human consumption or use by regulatory authorities such as the FDA. Its legality may vary depending on your country or region. It is essential to understand and comply with the laws and regulations of your jurisdiction before considering the use of BPC-157.
Is BPC-157 Safe?
While BPC-157 is generally considered safe, it is crucial to prioritize your safety and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment. Adverse effects associated with BPC-157 are minimal, with only mild and temporary discomfort reported at the injection site or minor gastrointestinal disturbances in some cases. However, individual responses may vary, and it is best to seek medical advice to ensure its safe use.
How Long Does BPC-157 Stay in Your System?
The exact duration of BPC-157 in the body is not well-established. However, based on available information, it is believed to have a relatively short half-life. The half-life refers to the time it takes for the concentration of a substance to reduce by half in the body. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance regarding the administration and duration of BPC-157.
Is BPC-157 a Steroid?
No, BPC-157 is not a steroid. It is a synthetic peptide derived from a naturally occurring protein called Body Protection Compound (BPC). BPC-157 works by promoting tissue regeneration and modulating various physiological processes in the body. It is important to note that peptides like BPC-157 have different mechanisms of action compared to steroids.
How Much Bacteriostatic Water to Mix with 5mg of BPC-157?
The appropriate amount of bacteriostatic water to mix with 5mg of BPC-157 may vary. It is recommended to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer or consult with a healthcare professional who can guide you on the correct reconstitution process for your specific product and desired dosage.
What Does BPC-157 Do for the Body?
BPC-157 has been the subject of scientific research exploring its potential advantages. It is believed to support tissue regeneration, promote joint and muscle health, aid in digestive system function, and contribute to the healing of wounds. However, it is important to note that research on BPC-157 is still ongoing, and its exact mechanisms and effects in the human body are yet to be fully elucidated.
Why is BPC-157 Banned?
To the best of our knowledge, BPC-157 is not banned by any regulatory authorities. However, its use may be restricted or prohibited in certain competitive sports organizations or athletic associations due to its potential performance-enhancing properties. It is advisable to check the rules and regulations of your specific sport or organization before considering the use of BPC-157.
Is BPC-157 Banned by FDA?
BPC-157 is not approved by the FDA for human use. The FDA regulates the use of substances for medical purposes and ensures their safety and efficacy through a rigorous approval process. As BPC-157 is considered a research peptide, it is important to understand that its use is not within the scope of FDA approval.
Does BPC-157 Really Work?
While anecdotal reports and preliminary research suggest Possible benefits of BPC-157, further scientific studies.
How is an intramuscular injection of BPC-157 administered?
Intramuscular injections involve injecting BPC-157 directly into a muscle belly. The process usually involves using a syringe with a needle of an appropriate length to reach the target muscle. It is essential to follow proper injection techniques to minimize the risk of complications.
What is the recommended body weight for BPC-157?
The recommended dosage of BPC-157, a synthetic peptide, is typically measured in micrograms or milligrams per kilogram of body weight. Standard dosages range from 250-500 mcg per kg. Always seek professional guidance before using BPC-157 or any other peptide to avoid potential adverse effects.
Gwyer D, et al. Acceleration of cutaneous wound healing by peptide analogues of BPC-157. Peptides. 2014;55:52-63.
Staresinic M, et al. Gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 accelerates healing of transected rat Achilles tendon and in vitro stimulates tendocytes growth. Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 2003;21(6):976-983.
Sikiric P, et al. Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 in trials for inflammatory bowel disease (PL14736). Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2011;17(16):1612-1632.
Vuksic T, et al. Gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 heals cysteamine-colitis and colon-colon-anastomosis and counteracts cuprizone brain injuries and motor disability. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 2013;64(5):597-612.
Krivic A, et al. Achilles detachment in rat and stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157: Promoted tendon-to-bone healing and opposed corticosteroid aggravation. Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 2006;24(5):982-989.
Sebecic B, et al. Osteogenic effect of a gastric pentadecapeptide, BPC-157, on the healing of segmental bone defect in rabbits: A comparison with bone marrow and autologous cortical bone implantation. Bone. 1999;24(3):195-202.
Huang T, et al. Systemic treatment with gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 enhances the reparative process of Achilles tendon rupture in rats. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. 2017;12(1):9.
Kopic S, et al. Enhancement by PL 14736 of granulation and collagen organization in healing wounds and the potential role of egr-1 expression. European Journal of Pharmacology. 2007;570(1-3):212-221.
Chang CH, et al. The promoting effect of pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on tendon healing involves tendon outgrowth, cell survival, and cell migration. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2011;110(3):774-780.
Wu X, et al. BPC 157 peptide promotes the survival of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells and enhances spinal cord injury repair. PLOS ONE. 2014;9(11):e112737.
Freitas D, et al. The effect of BPC-157, a peptide from gastric juice, on the healing of surgically induced Achilles tendonitis in rats. European Journal of Pharmacology. 2018;827:215-224.
Zhang R, et al. Therapeutic potential of BPC 157 peptide in subarachnoid hemorrhage: Anti-inflammation via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2020;19(1):15-22.
Wang Y, et al. Effects of pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on gastrointestinal motility disturbances induced by dopamine agonists. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2018;24(20):2302-2313.
Xue X, et al. Pentadecapeptide BPC 157, composed of 15 amino acids, ameliorates TNBS-induced IBD by modulating gut microbiota and increasing the production of short.
Report your symptoms and medical history to U.S.-licensed physician or nurse practitioner for evaluation
Report your symptoms and medical history to U.S.-licensed physician or nurse practitioner for evaluation
Report your symptoms and medical history to U.S.-licensed physician or nurse practitioner for evaluation